Roam Research is a friction-free, note-taking and knowledge-management application. It’s getting a lot of attention, and the label “game changer” has been used. You’re likely reading this article because you’ve heard the hype and are wondering if it’s true, and whether its features are a good fit for your needs.
At first glance, it appears to be a Workflowy-type online outliner, but first impressions can be deceptive. There’s a lot more power under the hood, such as the capability to create a network of knowledge that connects your thoughts using links and backlinks.
It’s a flexible tool that can be used for many tasks, including note taking and knowledge management, writing and outlining, journalling, GTD, research, and more. Developers are using it to explore ideas, create documentation, and log issues.
The more you store in it, the more useful it becomes. It’s not yet one of my primary tools, but it stands a good chance of becoming one. Perhaps it will become one of yours as well.
Personal Knowledge Management Is Hotting Up
I’ve been a little disillusioned with the personal knowledge management space over the last few decades. In the early, wild days of personal computing, “second brain” applications offered interesting and unique ways of viewing and manipulating your data:
- Ecco Pro used a combination of tabs, outlines, and columns. Each column was a field in a relational database.
- InfoCentral allowed you to connect people, events, and objects in a way that could be viewed as an outline. Each connection allowed you to precisely define the relationship.
- DayINFO let you build impromptu fields and branches to describe each person and object. Each object could exist in multiple places within your network of knowledge.
Unfortunately, they were lobotomized in the 1990s. Many were purchased during the Office Suite Wars and dumbed down or abandoned because they didn’t appeal to the average, non-technical user. Promising newcomers have since arisen — Zoot and InfoQube, for example — but they haven’t gained much traction … until recently. Roam Research, Obsidian, Craft, and others are gaining loyal followings by offering enticing new features. Automatic backlinks is the one attracting attention.
What Is Roam Research?
Like all good apps, Roam Research is opinionated, written by Conor White-Sullivan to scratch his own itch. It’s an outliner with links and backlinks, is online-only, and intentionally expensive — to price it out of the reach of casual users.
It’s unusual in that it allows you to structure your data simultaneously from the top down and bottom up. Each page is an outliner, allowing you to impose structure on your information as you type, edit, and rethink. I love outliners and find Roam’s very fluid.
The ability to link separate notes also allows you to create structure from the bottom up as you notice relationships between your notes over time. This can lead to unexpected discoveries and is a central principle of the Zettelkasten method of note-taking, and one that Roam was built to encapsulate.
The methodology was created by the sociologist Niklas Luhmann as he used analog index cards to explore the relationships between ideas. It worked and was directly responsible for his prolific creation of around 70 books and 400 academic articles.
It’s built on the idea of anatomic notes written in your own words that contain just one idea. Structure is an afterthought and develops organically as you notice new relationships between your thoughts. You reference one note in another, and then create a backlink to the original note.
You can learn more by perusing Zettelkasten.de and reading the book How to Take Smart Notes, by Sonke Ahrens.
Roam Research Main Concepts
Here are the main concepts used by Roam Research. Use them as building blocks to design your own information system.
Outliner: each page is a single-pane outliner made up of hierarchical blocks of text and images. This encourages both anatomic and structured thinking. Command + Shift + Up and Down move blocks higher and lower. Tab and Shift + Tab change indentation. Command + Up and Down expand and contract the outline.

Find: the Find feature at the top of the page will find all pages containing a phrase. It also allows you to create a page with that name if one doesn’t already doesn’t exist, similar to the way nvAlt works.
Filter: the Filter icon allows you to show or hide blocks containing specific links on a page.
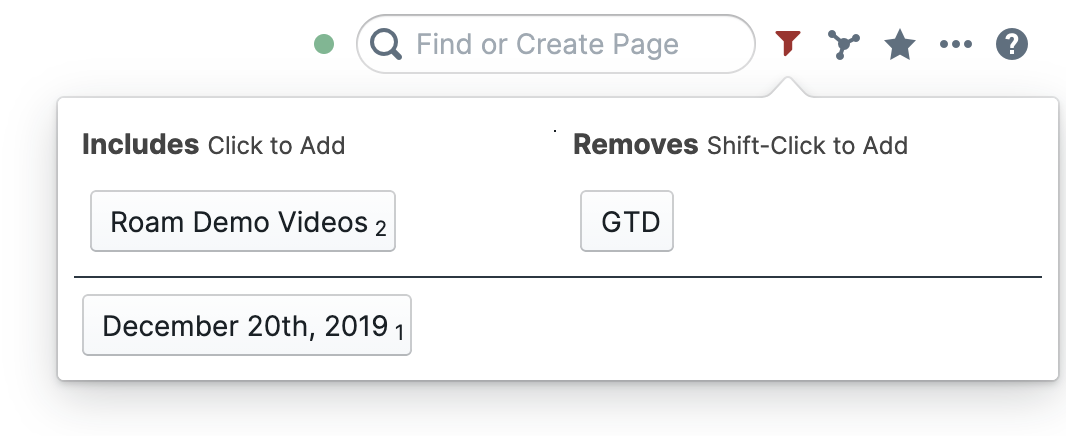
Boolean queries: queries are embedded in the outline and are a way you can ask Roam Research questions. Logical Boolean operators like “and”, “or”, and “not” are supported. Matching hits are pulled into the outline.
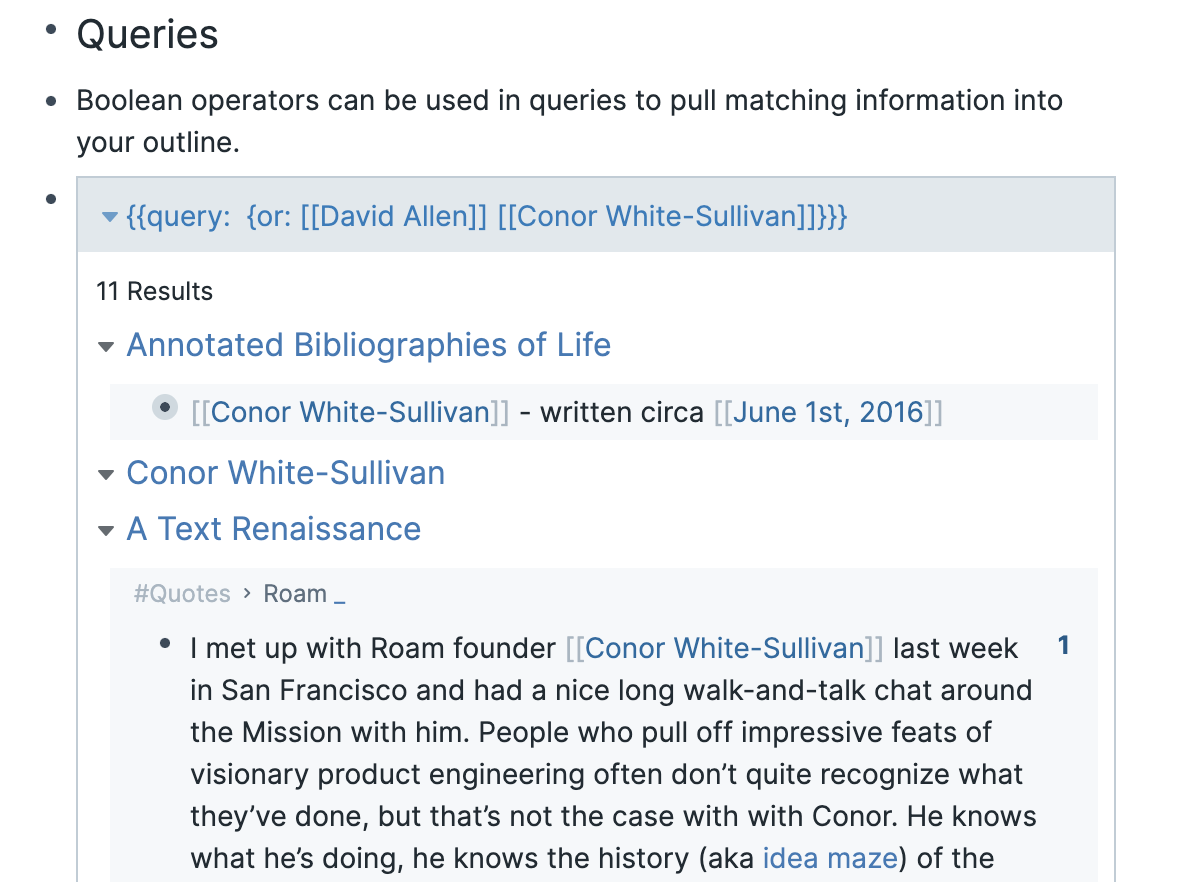
Links and backlinks: links allow you to create a system of networked thought or a personal wiki. You link to another page using [[wikilinks]] and a new page is created if it doesn’t already exist. Backlinks are automatically generated, and the context of the link is included, adding helpful information to the page.

Tags: in Roam, tags are similar to pages, in that every tag automatically gets its own page. As with pages, every page that contains the tag is listed as a backlink.

Embed: blocks from one part of Roam can be referenced or embedded somewhere else. You can also embed pages, websites, videos, and more.
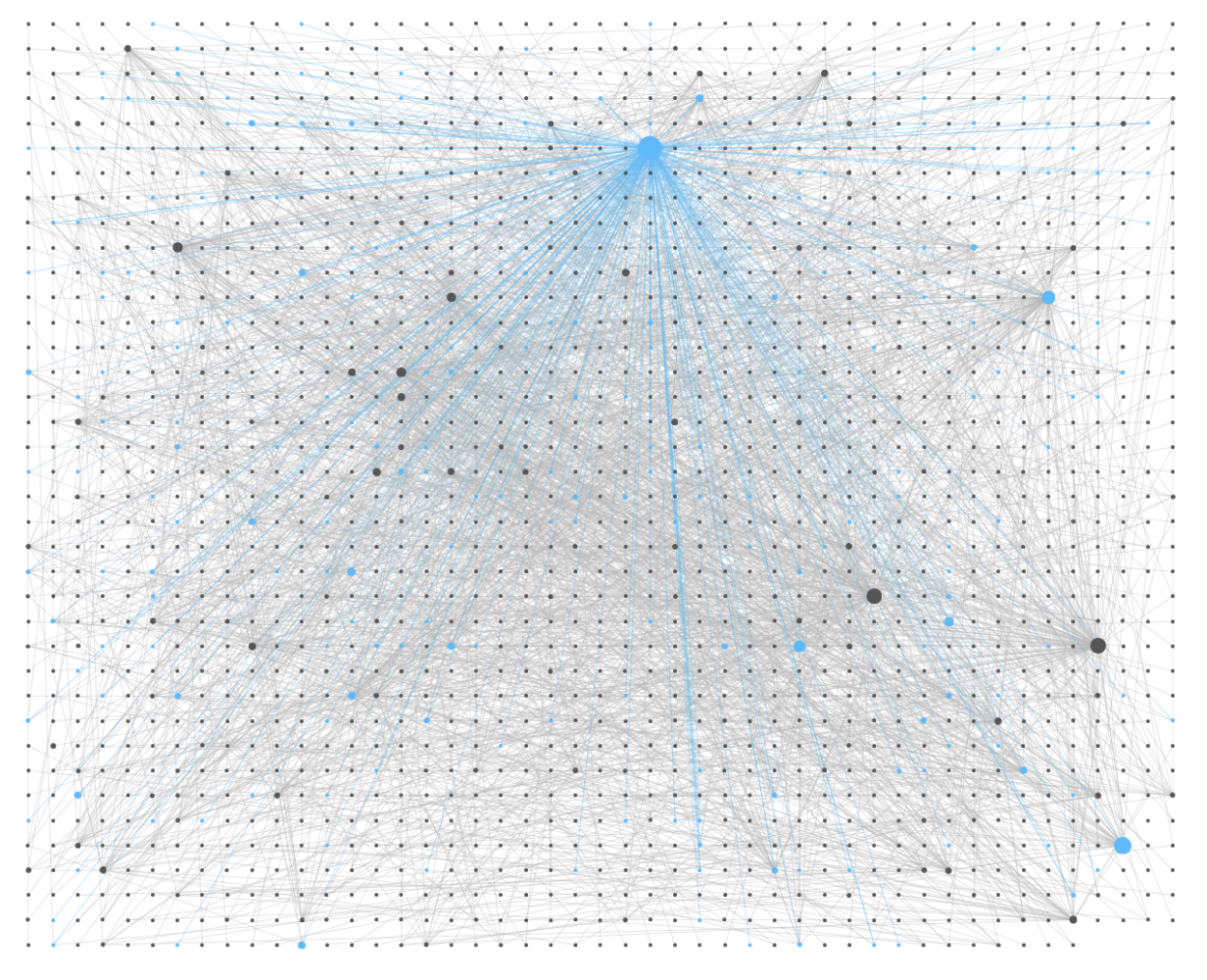
Graph: a digital representation of the relationships between pages. Clicking on one page will color all related pages blue. Double-clicking a page will open it.

Markdown: Markdown is supported and is hidden until you edit a block. Unfortunately, it’s not quite standard. While **bold** text is created with double asterisks, __italics__ requires double underscores rather than single underscores or asterisks. Dynalist does the same and is probably the inspiration here.
Latex notation: you can add mathematical notation to Roam by enclosing Latex code inside double dollar symbols.
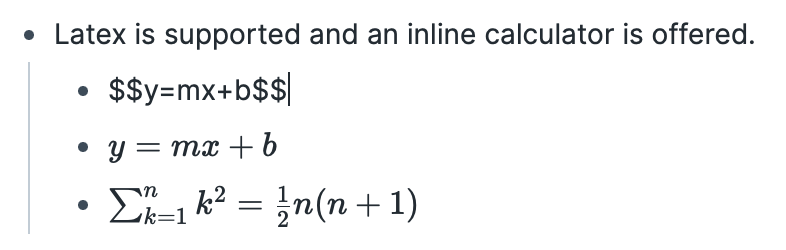
Code blocks: Roam offers code blocks with syntax highlighting. Start a code block with triple back ticks and a single back tick is used for inline code.

Slash menu: like Notion, Slack, and others, Roam offers quick access to features through a slash menu.

Sidebars: sidebars allow you to access information elsewhere in Roam without losing your spot. The right and left pane can be shown or hidden using Command + / and Command + respectively. Shift-click to open a link in the sidebar.
Components: Roam’s features can be extended using components, which currently include an inline calculator ({{calc: 4 + 5}}), word count, date picker, block/page embed, PDF embed, video embed, website embed, encrypted text, Kanban board, mentions, Pomodoro timer, and tables.
Continue reading
A Beginner’s Guide to Roam Research
on SitePoint.
